-

Comparison of Associated Autoimmune Disease Diagnoses in Myasthenia Gravis and Multiple Sclerosis Patients
Alecca Como, Jacob Keeley, and Daniel Menkes
Publication Date: 5-2024
Autoimmune diseases often co-exist given the non-specific nature of the immune response. For example, myasthenia gravis [MG], a well-established autoimmune disease, has a 2.36-fold increased risk of developing thyroid diseases as compared to normal controls. 1,2 In contrast, multiple sclerosis [MS] is a disorder in which the immune system subserves an important pathogenic role, although there is insufficient evidence to definitively classify it as an autoimmune disease. 3,4 Since the etiology of MS has yet to be identified, and the specific autoimmune mechanism requires further elucidation, the comparison of its coassociated autoimmune diseases with that of a well-studied neuroautoimmune disease, MG, may provide direction for future studies looking into the pathophysiology and autoimmune mechanism of MS. In order to further explore the coexistence of autoimmune disorders, this study compared the association of concordant autoimmune diseases between MG and MS patients, using migraine, a non-autoimmune neurological disorder, as a control group.
-

Targeted-Sequencing Evaluation for FZD4 Variants in Familial Exudative Vitreo-Retinopathy
Mary Drekh, Wendy Dailey, Vincent Le, Savyo Krikor, Kimberly A. Drenser, and Kenneth P. Mitton
Publication Date: 5-2024
- The Familial hereditary vision loss disease may present with symptoms including retinal detachment, folding, neovascularization, or vitreous hemorrhage due to peripheral retina avascularity.
- The manifestation of FEVR genetically has been associated with a loss of function mutation of the Wnt/bcantenin-signaling pathway involving 7 genes (FZD4, NDP, CTNNB1, KIF11, LRP5, TSPAN12, and ZNF408). In our patient population of 72 individuals the distribution of FZD4 gene variants leading to FEVR has been recorded.
- The Frizzled4 gene (FZD4) codes for the G-coupled protein receptor and effects Wnt/b-cantenin-signaling pathway In endothelial cells.
- What frequency of FEVR from our patient pool will have FZD4 variants known to be protein altering? Will novel mutants of this gene have hereditary pathogenic effects?
- Due to the variable severity of FEVR even within a single family, it is possible that having protein-altering variants in more than one of these FEVR-associated genes including FZD4 is a contributing factor to phenotypic variability. What is the frequency of Multigenic variants leading to FEVR?
-
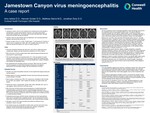
Jamestown Canyon Virus Meningoencephalitis: A Case Report
Amy Ishbia, Hannah Guide, Matthew Sierra, and Jonathan Doty
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Jamestown Canyon virus is a rare mosquito-borne orthobunyavirus that typically is asymptomatic or causes mild symptoms. However, it can rarely cause severe neuroinvasive disease [2,5]. The primary hosts include white-tailed deer, although moose, elk, and bison can also be hosts [2].
Typically, cases are seen between April and September, with a bimodal distribution peaking in spring and late summer [2].
Number of cases in the U.S. in 2024: 16 total cases, 11 neuroinvasive [1]. Number of cases in the U.S. between 2011-2023: 308, with 10 deaths, 206 neuroinvasive. One case was reported from Alpena, MI, where our patient resided [1].
-
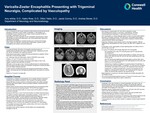
Varicella-Zoster Encephalitis Presenting with Trigeminal Neuralgia, Complicated by Vasculopathy
Amy Ishbia, Kathy Ross, Dillon Yaldo, Jacob Conroy, and Andrea Stoner
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
VZV is a herpesvirus that causes chickenpox before laying dormant and having the potential to reactivate to cause myelitis, encephalitis, or vasculopathy.
Encephalitis occurs in less than 0.1% of cases; however accounts for 90% of neurologic complications from VZV.
Vasculopathy is a rare complication of VZV encephalitis characterized by vessel wall damage and transmural inflammation with multinucleated giant cells and/or epithelioid macrophages.
Vasculopathy has significant morbidity/mortality due to ischemic/hemorrhagic stroke, spinal cord infarction, temporal artery inflammation, ischemic cranial neuropathies and cerebral venous thrombosis.
-
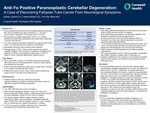
Anti-Yo Positive Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration: A Case of Discovering Fallopian Tube Cancer From Neurological Symptoms
Sydney Jacobs, Alaina Skotak, and Inna Sta Maria
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Paraneoplastic syndromes are rare neurological disorders associated with cancer at distant tumor sites. Prevalence is ~1-3% of all cancers, with an estimated 17,099 cases in the US in 2021.
Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration (PCD) is one subtype, primarily associated with gynecological and breast cancer, especially in women older than 60.2
Can cause significant functional impairment (e.g. abrupt onset truncal ataxia, room-spinning dizziness, dysarthria, and diplopia).
Neurological symptoms often precede cancer diagnosis.
Pathophysiology of PCD: Tumor-induced autoimmunity against cerebellar antigens.4 About 30 types of antibodies, one being anti-Yo antibody (or Purkinje cell cytoplasmic antibody type 1, (PCA-1)) acting on human cerebellar degeneration-related protein.
-

Seeing Double An atypical presentation of RCVS
Lauren Kassab, Alexander Ismail, and Jonathan Doty
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS) is a syndrome characterized by reversible, multifocal narrowing of the cerebral arteries and a thunderclap headache (reaching a peak intensity within one minute). A less severe headache, or lack thereof, is rare (1). Additional neurologic symptoms are typically dependent on the sequelae of focal intracranial stenosis, including ischemia, PRES, and IPH. Common precipitants are cannabis, SSRIs, alcohol, cocaine, and eclampsia. Depending on the inciting cause, presentations can also widely vary over a course of months - years. Diagnosis can be pervasive, as noninvasive vascular imaging has an 80% sensitivity (2). Definitive diagnosis is made with angiogram, with vasoconstriction in at least two vessels and resolution in three months, as well as negative serology and CSF markers for vasculitis. Treatment involves identifying and reversing the offending agent, and in some cases calcium channel blockers.
-

Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS) of the Centromedian Nucleus (CMN) of the Thalamus for the Treatment of Drug Resistant Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy (IGE)
Angelique Manasseh, Hannah Guider, Brooklynn Bondy, Sanjay Patra, David Burdette, M. Ayman Haykal, Nour Baki, Ashleigh Terrell, Michael Staudt, Christopher Parres, and Andrew Zillgitt
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE) accounts for nearly 1/3 of all epilepsies.
Approximately 20-30% of people with IGE are refractory to adequate anti-seizure medication trials.
RNS implantation is a unique closed-loop neuromodulation therapy, and case reports as well as case series have demonstrated improved seizure control in patients with drug resistant IGE.
More recently, targeting the centromedian nucleus of the thalamus with RNS has been explored as a potential surgical treatment option for patients with drug resistant IGE.
-
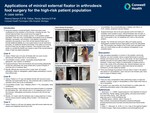
Applications of Minirail External Fixator in Arthrodesis Foot Surgery for the High-Risk Patient Population: A Case Series
Reema Naman
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Since the inception of external fixation, there have been many modifications to the utilization of the devices, including the size. The minirail external fixator has evolved since the usage for bracymetatarsia into more complex devices. In the podiatric patient population, there are many comorbidities encountered such as diabetes, idiopathic neuropathy, and smoking. In the diabetic neuropathic population the purpose of use of the minirail external fixator was to provide additional stability as a mini-superconstruct as per Sammarco principles. An additional benefit of the fixator is the option of removing the pins if there are any signs of infection. The purpose of this case series is to exhibit the benefit and myriad of uses of the minirail external fixator in high-risk patient population.
-
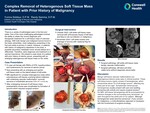
Complex Removal of Heterogenous Soft Tissue Mass in Patient with Prior History of Malignancy
Yumna Siddiqui and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
There is a variety of pathologies seen in the foot and ankle. One of the more challenging pathologies involves the ability to obtain the correct diagnosis and therapeutic treatment for a soft tissue mass of unknown etiology. With both benign and malignant tumors found in the lower extremities, most malignancy presenting in the foot and ankle is primary in nature. However, in patients with history of malignancy elsewhere in the body, a possible secondary metastatic tumor should always be a differential. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment is of upmost importance. We present a case study of a patient with prior history of uterine cancer, presenting with an enlarging heterogenous soft tissue mass on her ankle.
-
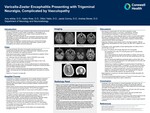
Varicella-Zoster Encephalitis Presenting with Trigeminal Neuralgia, Complicated by Vasculopathy
Amy Ishbia, Katherine Ross, Dillon Yaldo, Jacob Conroy, and Andrea Stoner
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
VZV is a herpesvirus that causes chickenpox before laying dormant and having the potential to reactivate to cause myelitis, encephalitis, or vasculopathy [1,4]. ▪ Encephalitis occurs in less than 0.1% of cases; however accounts for 90% of neurologic complications from VZV [2].
Vasculopathy is a rare complication of VZV encephalitis characterized by vessel wall damage and transmural inflammation with multinucleated giant cells and/or epithelioid macrophages.
Vasculopathy has significant morbidity/mortality due to ischemic/hemorrhagic stroke, spinal cord infarction, temporal artery inflammation, ischemic cranial neuropathies and cerebral venous thrombosis [2].
-
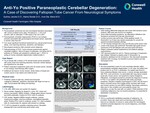
Anti-Yo Positive Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration: A Case of Discovering Fallopian Tube Cancer From Neurological Symptoms
Sydney Jacobs, Alaina Skotak, and Inna Sta Maria
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
Paraneoplastic syndromes are rare neurological disorders associated with cancer at distant tumor sites. Prevalence is ~1-3% of all cancers, with an estimated 17,099 cases in the US in 2021.
▪ Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration (PCD) is one subtype, primarily associated with gynecological and breast cancer, especially in women older than 60.2
▪ Can cause significant functional impairment (e.g. abrupt onset truncal ataxia, room-spinning dizziness, dysarthria, and diplopia).
▪ Neurological symptoms often precede cancer diagnosis.
▪ Pathophysiology of PCD: Tumor-induced autoimmunity against cerebellar antigens.4 About 30 types of antibodies, one being anti-Yo antibody (or Purkinje cell cytoplasmic antibody type 1, (PCA-1)) acting on human cerebellar degeneration-related protein.
-

Seeing Double An Atypical Presentation of RCVS
Lauren Kassab, Alex Ismail, and Jonathan Doty
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS) is a syndrome characterized by reversible, multifocal narrowing of the cerebral arteries and a thunderclap headache (reaching a peak intensity within one minute). A less severe headache, or lack thereof, is rare (1). Additional neurologic symptoms are typically dependent on the sequelae of focal intracranial stenosis, including ischemia, PRES, and IPH. Common precipitants are cannabis, SSRIs, alcohol, cocaine, and eclampsia. Depending on the inciting cause, presentations can also widely vary over a course of months - years. Diagnosis can be pervasive, as noninvasive vascular imaging has an 80% sensitivity (2). Definitive diagnosis is made with angiogram, with vasoconstriction in at least two vessels and resolution in three months, as well as negative serology and CSF markers for vasculitis. Treatment involves identifying and reversing the offending agent, and in some cases calcium channel blockers.
-

Evaluation of peri-operative antibiotic prophylaxis in patients undergoing total joint hip or knee arthroplasty
Heidi Klotz, Lauren Kassab, Muddasser Saiyed-Javed, Sandra Hartnagle, and Sapna Shah
Publication Date: 12-6-2023
-

Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS) of the Centromedian Nucleus (CMN) of the Thalamus for the Treatment of Drug Resistant Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy (IGE)
Angelique Manasseh, Hannah Guider, Brooklynn Bondy, Sanjay Patra, David Burdette, Ayman Haykal, Nour Baki, Ashleigh Terrell, Michael Staudt, Christopher Parres, and Andrew Zillgitt
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
Idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE) accounts for nearly 1/3 of all epilepsies1
▪ Approximately 20-30% of people with IGE are refractory to adequate anti-seizure medication trials1
▪ RNS implantation is a unique closed-loop neuromodulation therapy, and case reports as well as case series have demonstrated improved seizure control in patients with drug resistant IGE1
▪ More recently, targeting the centromedian nucleus of the thalamus with RNS has been explored as a potential surgical treatment option for patients with drug resistant IGE
-
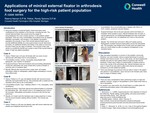
Applications of Minirail External Fixator in Arthrodesis Foot Surgery for the High-Risk Patient Population A Case Series
Reema Naman and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
Since the inception of external fixation, there have been many modifications to the utilization of the devices, including the size. The minirail external fixator has evolved since the usage for bracymetatarsia into more complex devices. In the podiatric patient population, there are many comorbidities encountered such as diabetes, idiopathic neuropathy, and smoking. In the diabetic neuropathic population the purpose of use of the minirail external fixator was to provide additional stability as a mini-superconstruct as per Sammarco principles. An additional benefit of the fixator is the option of removing the pins if there are any signs of infection. The purpose of this case series is to exhibit the benefit and myriad of uses of the minirail external fixator in high-risk patient population.
-
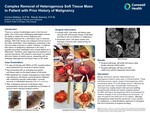
Complex Removal of Heterogenous Soft Tissue Mass in Patient with Prior History of Malignancy
Yumna Siddiqui and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
There is a variety of pathologies seen in the foot and ankle. One of the more challenging pathologies involves the ability to obtain the correct diagnosis and therapeutic treatment for a soft tissue mass of unknown etiology. With both benign and malignant tumors found in the lower extremities, most malignancy presenting in the foot and ankle is primary in nature. However, in patients with history of malignancy elsewhere in the body, a possible secondary metastatic tumor should always be a differential. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment is of upmost importance. We present a case study of a patient with prior history of uterine cancer, presenting with an enlarging heterogenous soft tissue mass on her ankle.
-
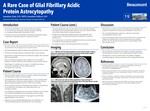
A Rare Case of Autoimmune Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Astrocytopathy
Jonathan Doty and Jonathan Fellows
Publication Date: 5-2022
• Autoimmune glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) astrocytopathy is a rare autoimmune inflammatory disorder typically manifesting as a meningoencephalomyelitis first identified in 20161 . • Awareness of the clinical manifestations and hallmark radiographic findings is important for appropriate diagnostic testing and treatment.
-

Inflammatory Myopathy and Myasthenia Gravis Overlap Syndrome
Brandon Vieder, Nick Olen, William Boudouris, and Robert Pierce
Publication Date: 5-2022
• We present the case of a rare, complex process of overlap between Myasthenia Gravis and Inflammatory Myositis. • Less than 50 cases have been reported, and do not respond as readily to typical treatments
-

Isolated Bilateral Cerebellar Restriction Diffusion: An Atypical Presentation of Wernicke’s Encephalopathy
Diana Zaituna and Angelique Manasseh
Publication Date: 5-2022
• Wernicke encephalopathy is a neurologic complication of thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency • Familiarity with clinical presentation and MRI findings are important for rapid diagnosis • Treatment is with emergent thiamine supplementation to prevent morbidity (i.e. Korsakoff syndrome) and mortality1 • We present a case of Wernicke’s encephalopathy with the rare MRI brain finding of isolated cerebellar diffusion restriction, which has only been seen in one other case report, per our extensive literature review
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.

