-

Purr-Ils of the Liver: A Case of Mash Cirrhosis Complicated by Disseminated Pasteurella
Joanna Henry, Alaa Abujame, Cameron Hubbard, Angela Shermetaro, James Hebden, Hussein Bazzy, Jared Grodman, Katie Sumnicht, and Christopher Cooley
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
Pasteurella Multicoda is a gram-negative coccobacillus that is commensal to mammals such as domesticated pets and transmitted to humans by scratches or bites. The extent of infection is often limited to soft tissue, bone, and joint.
Disseminated infection by P. multicoda infrequently is typically associated with peritoneal dialysis.
We present a case of disseminated P. multocida infection with bacteremia and peritonitis in a patient with NASH Cirrhosis
-
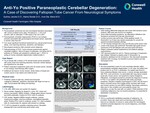
Anti-Yo Positive Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration: A Case of Discovering Fallopian Tube Cancer From Neurological Symptoms
Sydney Jacobs, Alaina Skotak, and Inna Sta Maria
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
Paraneoplastic syndromes are rare neurological disorders associated with cancer at distant tumor sites. Prevalence is ~1-3% of all cancers, with an estimated 17,099 cases in the US in 2021.
▪ Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration (PCD) is one subtype, primarily associated with gynecological and breast cancer, especially in women older than 60.2
▪ Can cause significant functional impairment (e.g. abrupt onset truncal ataxia, room-spinning dizziness, dysarthria, and diplopia).
▪ Neurological symptoms often precede cancer diagnosis.
▪ Pathophysiology of PCD: Tumor-induced autoimmunity against cerebellar antigens.4 About 30 types of antibodies, one being anti-Yo antibody (or Purkinje cell cytoplasmic antibody type 1, (PCA-1)) acting on human cerebellar degeneration-related protein.
-

Readmission Rates In Complex Cases Does Review of AVS with Patients/Families Lead to Lower Readmissions?
Nick Leventis
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
-

Development and Evaluation of a Peer Education-Based Ultrasound Curriculum with Emphasis on Clinical Reasoning
Nisha Patel and Arati Kelekar
Publication Date: 5-2023
Point-of-care ultrasonography (POCUS) is being increasingly incorporated in pre-clerkship physical diagnosis courses. However, the development of such a curriculum at many medical schools is limited by financial constraints, the availability of trained faculty, and the recent COVID-19 pandemic. Here, we describe an optional POCUS curriculum that circumvents these barriers while still providing basic image acquisition skills and pathophysiological correlations.
-

Changes in Electrocardiographic and Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Parameters Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Elizabeth Seeley, Luai Madanat, and Nishaki Mehta
Publication Date: 5-2023
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is known to cause conduction abnormalities leading to the need for permanent pacemaker implantation. However, the impact of TAVR-related conduction abnormalities on cardiac implantable electronic device (CIED) parameters in patients with preexisting devices is not known. We sought to investigate and describe changes in EKG and CIED parameters following TAVR in patients with preexisting CIEDs.
-

A Rare Case of Radial Arteriovenous Formation After Transradial Cardiac Catheterization
Barbara Senger, Hassan Eidy, Andrew Gray, and Robert Grodman
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
In the United States, more than one million cardiac catheterization procedures are performed each year for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
▪ Right heart catheterizations allow for direct measurement of right-sided cardiac and pulmonary hemodynamics while left heart catheterizations provide a diagnostic and therapeutic role in those with coronary artery disease.
▪ In 1989, Lucien Campeau proposed the use of a smaller caliber catheter to access the small radial artery as a way to reduce the rates of bleeding complications.
▪ Advantages of utilizing the transradial artery (TRA) approach over the transfemoral artery (TFA) approach include: – Improved patient quality-of life metrics. – Reduced major bleeding and access site complications. – Lower total hospital costs.
▪ Access-site complications including radial artery occlusion and arteriovenous fistula (AVF) formation from TRA are rare and usually of minimal clinical impact.
▪ AVF may present with pain and edema at the puncture site, a pulsatile thrill, and/or visible dilated superficial veins.
-

Liver Injury, Renal Failure, and Pancytopenia after Radioactive Iodine Treatment for Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma A Case Report
Angela Shermetaro, Grant Hupp, and Jordan Bushman
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
Radioactive Iodine (RAI) has been used for diagnosis and treatment of thyroid carcinomas since the 1940’s. Some known side effects include gastritis, radiation thyroiditis, and bone marrow suppression. However, there are minimal reports on radioactive iodine causing drug induced liver injury (DILI) and renal failure.
To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of both hepatic injury and renal failure following RAI treatment.
We describe an 83-year-old female who developed DILI and renal failure after radioactive iodine ablation.
-
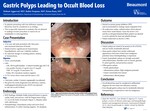
Gastric Polyps Leading to Occult Blood Loss
Nishant Aggarwal, Rabin Neupane, and Ketan Rana
Publication Date: 10-2022
Introduction
In patients presenting with iron deficiency anemia, blood loss must be considered as an etiology. This is especially important in patients who are planned to undergo invasive procedure or need to be on antiplatelets or anticoagulation.
Discussion
Gastric polyps are noted to be present in 6% of EGDs, and are mostly incidentally detected. Many gastric polyps have similar endoscopic appearances and some of them have malignant potential, hence histolopathology is important. Gastric hyperplastic polyps are strongly associated with inflammatory disorders such as chronic gastritis, H. pylori gastritis, and pernicious anemia.1 Other gastric polyps: – Fundic gland polyps – Adenomatous polyps: High malignant potential – Gastric neuroendocrine tumors – Inflammatory fibroid polyps
Conclusion
Occult blood loss must be considered in differential diagnosis for new onset iron deficiency anemia. Even though gastric polyps may be incidentally detected, histopathology is important to rule out malignancy.
-
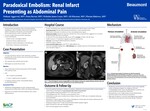
Paradoxical Embolism: Renal Infarct Presenting as Abdominal Pain
Nishant Aggarwal, Dana Rector, Nicholas J. Lazar, Ali Khreisat, and Florian Bukovec
Publication Date: 10-2022
Introduction
Paradoxical thromboembolism refers to thromboembolism originating in venous circulation which traverses directly into systemic circulation in the presence of an intracardiac (such as patent foramen ovale) or pulmonary shunt. Can have variable clinical presentation depending on site of embolization – Embolic stroke: neurological deficits – Intestinal ischemia: abdominal pain – Peripheral arterial embolization: acute limb pain – Renal infarct: flank pain and hematuria.
Conclusion
Simultaneous arterial and venous thrombosis requires hypercoagulable workup, including investigation for malignancy, infection, or thrombophilia. Rarely, venous thromboembolism can directly cause arterial thrombosis by paradoxical embolization. Renal infarction is rare. Usually presents as acute abdominal pain and AKI in patients with risk factors for thrombosis. High index of suspicion is crucial for timely diagnosis given patients may benefit from percutaneous endovascular therapy, if indicated.
-

Improving Appropriate Utilization of Echocardiography in the Workup of Syncope
Sam Alsabti, Alexander Schick, Jacob Morton, Inna Sta. Maria, Devika Aggarwal, Matthew Sullivan, Pradeep Kaminoulu, Nicholas Maddens, Justine Nasr, and Alexandra Halalau
Publication Date: 10-2022
Introduction
20-50% of all medical imaging is of low value or inappropriate. Echocardiography (echo) is a safe and diagnostic test that provides reliable information about the heart but comes at a cost. Current ACC/AHA guidelines only recommend use of echocardiography in syncope when there is suspected structural heart disease based on cardiac history, physical exam, or electrocardiogram.
Objectives
To identify appropriate utilization rates of echocardiography in the workup of syncope. • To improve appropriate resource utilization by implementing a guideline-based, PDSA (Plan-Do-Study-Act) Quality Improvement protocol (Figure 1) using informational material placed in and around commonly used resident working areas (Figure 2).
Conclusion
Echo has a low diagnostic yield when evaluating patients with syncope. • An increase in the appropriate utilization of this resource may increase its accessibility to clinical settings where it is more urgently needed, reduce hospital costs and length of stay, and lower the financial burden incurred by the patient
-

Death Exposure Influence on Medical Students’ Attitudes Toward End-of-Life Care
Sara J. Barlow, Nelia Alfonso, and Jason A. Wasserman
Publication Date: 5-5-2022
INTRODUCTION
Advance directives help guide individuals and their families in making end-of-life decisions that physicians must respect and carry out on behalf of patients to provide optimal care that aligns with their wishes. The facilitation of end-of-life care and the application of advance directives are impacted by physicians’ attitudes and knowledge regarding this topic. Current studies focus on the perspective that practicing physicians have toward advance directives. Our goal is to examine the end-of-life preferences of medical students at Oakland University William Beaumont (OUWB) School of Medicine before and after clinical exposure to better appreciate how and when opinions regarding end-of-life care develop during physician’s education. -
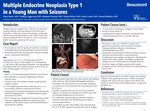
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 in a Young Man With Seizures
Nitya Batra, Nishant Aggarwal, Shailesh Niroula, Daniel Misra, Peter Czako, and Daniel Shelden
Publication Date: 10-2022
Introduction
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is an autosomal dominant disorder involving mutation of the MEN1 gene. Clinically it is defined by tumors of the pituitary, parathyroid, and the entero-pancreatic endocrine cells. Other tumors have been associated with MEN1. We present a case of a previously healthy young man presenting with seizures.
Discussion
We present a classic case of MEN1 in a patient with significant family history with the presence of primary hyperparathyroidism, pituitary microadenoma, and duodenopancreatic NETs. • Interestingly, rare presentation of MEN1 as refractory seizures have been reported secondary to hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, but our patient was euglycemic with appropriate levels of insulin and C-peptide. This suggests an alternative etiology that is not well documented in available literature. • Given the complex and highly specialized skills needed to diagnose and treat MEN1, involvement of a multidisciplinary team is vital.
Conclusion When the clinical suspicion for MEN1 is high, endocrinology evaluation with appropriate laboratory workup and targeted imaging of the typical endocrine organs as described for this patient are advised with careful multidisciplinary management and follow-up.
-

A Novel Case of Babesiosis in a Gardener
James Benke, Jay Shah, and David Lang
Publication Date: 5-2022
• Babesiosis serious health concern in Northern and Midwestern US • Transmitted through tick, Ixodes scapularis • Presents with fever and several non-specific complaints • Diagnosis - Blood smears, DNA by PCR, and anti-body titers • Can be fatal when left untreated • Treatment - IV antibiotics • This case discusses a severe presentation of babesiosis in a gardener, who survived with a prolonged course of antibiotics
-

Apical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A Rare Variant of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathies
Alexandra Corrado-Kittel, Diana DeAngelis, Katharine Glover, and Gregory Hazergian
Publication Date: 5-2022
Introduction • AHCM is a rare morphological variant of hypertrophic cardiomyopathies • The AHA/ACC defines hypertrophic cardiomyopathy as left ventricular hypertrophy in the absence of abnormal loading conditions, or other cardiac, systemic, or other metabolic disease capable of producing the magnitude of hypertrophy observed on echocardiogram • Regardless of the morphology, understanding workup, management and follow up are crucial
-

Cannabis and Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Case Report Exploring Potential Links
Fawaz Habba, Michael Hoban, and Scott Searing
Publication Date: 5-2022
Introduction • Cannabis is a commonly abused drug in the United States. It is paramount that physicians understand the risks of its use that may impact patient safety, particularly its effects on the cardiovascular system. • There are two cannabinoid receptors which the active component of marijuana, delta-9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), acts on: Cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1 ) and cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2 ). • THC causes stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system while inhibiting the parasympathetic nervous system. • While the precise pathophysiology behind myocardial infarction in patients consuming marijuana is unknown, it is postulated that sudden coronary occlusion is likely due to plaque disruption caused by the hemodynamic alterations cannabis causes on the cardiovascular system.
-
Incidental Pathogenic Fibrin-Associated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Found During Aorto-Biiliac Bypass
Peter Habib, Thomas Serena, Caitlin Flynn, Aaron Hartkop, Elizabeth Wey, David Lang, and Eugene Laveroni Jr
Publication Date: 5-2022
Introduction • Fibrin-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (FA-DLBCL) is an extremely rare form of Epstein-Barr virus positive (EBV+) non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. • This case presents a rare and unique presentation of a pathological non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
-

Exploring the Effects of Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction on Pre-Clinical Medical Students: A Qualitative Methods, Longitudinal Pilot Study
Alyssa Heintschel, Scott Sabbagh, Patrick Herndon, Michael Moussa, and Ruth Lerman
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction has become an increasingly popular practice in healthcare-affiliated populations. MBSR is a course designed to promote mindfulness and awareness within oneself through a combination of formal and informal practices. Studies suggest healthcare workers are at higher risk of experiencing stress and burnout; this is prevalent among pre-clinical medical students due to the rigorous nature of medical school coursework. The primary objective of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness and feasibility of implementing an MBSR program to facilitate improvements in key areas of mental health among medical students throughout their training. -

Investigating the Effectiveness of a Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction Course Within Healthcare: A Qualitative Methods Study
Patrick Herndon, Michael Moussa, Alyssa Heintschel, Scott Sabbagh, and Ruth Lerman
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
Mindfulness practice has emerged as a promising means to address stress in healthcare workers (HCW). Virtually all HCW studies of the standardized, validated Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) curriculum have been conducted using homogeneous (HCW only) populations. This work examines the novel approach of comparing the effects of heterogeneous MBSR classes: HCW, oncology patients and family members (HCW-HE) as compared to homogeneous classes HCW and their family members only (HCW-HO) -

Asymptomatic chronic sinusitis as an atypical presentation of meningitis
David Hwang, Laura Azzouz, Zeshan Choudhry, and Benjamin Rossi
Publication Date: 5-2022
Introduction We present a unique case report of asymptomatic acute on chronic pansinusitis with parameningeal involvement as an atypical presentation of meningitis with associated pyrexia, nuchal rigidity, and headaches. Following initial admission, patient clinically deteriorated subsequently requiring emergent surgical debridement with ENT with cultures demonstrating fusobacterium nucleatum. This case presentation is of unique interest given long term neurological sequelae which can manifest as a result of delayed therapy, both medical and surgical, which includes but is not limited to permanent vision loss, ataxia, gait difficulty, and long standing sensorimotor deficits. We hope to provide additional educational resources given the lack of clear standard treatment protocols for meningitis secondary to sinusitis and rare clinical scenario
-
PEG Tube: Dealing With Transcolonic Misplacement
Marko Kozyk, Kateryna Strubchevska, and Mihaela Batke
Publication Date: 10-2022
Introduction
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tube acts as the favorable route of feeding and nutritional support in patients with a functional gastrointestinal system who require long-term enteral nutrition, generally beyond 4 weeks. As PEG tube provides direct percutaneous access to the stomach, another indication for PEG placement includes stomach decompression. PEG tube placement is a relatively safe procedure; however, complications sometimes occur.
Discussion
Complications of PEG: • Hemorrhage • Aspiration • Inflammation • Infections • Misplacement • Formation of fistulas Misplacement results from juxtaposition of the colon between the stomach and the skin during the PEG insertion, resulting in a feeding tube passing through the colon, usually the transverse colon, before being anchored in the stomach.
Prevention of PEG-tube misplacement: • Adequate air insufflation of the stomach can help prevent this complication by displacing the colon away from the path of the PEG tube
Management of PEG tube misplacement: • Surgical (in the presence of peritonitis) • Endoscopic (in the absence of peritonitis) • Percutaneous removal of the tube may result in stercoral peritonitis or colocutaneous fistula.
-

Investigating the Effects of a Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction Course on a Grouping of Oncology Patients, Health Care Workers and their Families on Measures of Stress and Burnout in Health Care Workers: A Randomized Control Trial
Michael Moussa, Patrick Herndon, Alyssa Heintschel, Scott Sabbagh, and Ruth Lerman
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) can improve the mental health of health care workers (HCW). How will the inclusion of oncology patients (OP) in MBSR classes for HCW affect the mental health of HCW? -

Acquired Acrodermatitis Enteropathica Presenting as Confusion and Desquamating Maculopapular Rash
Nazli Begum Ozturk, Ali Khreisat, Luai Madanat, and Lynda Misra
Publication Date: 10-2022
-

Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction for Pre-Clinical Medical Students: Exploring Efficacy and Benefit
Scott Sabbagh, Alyssa Heintschel, Patrick Herndon, Michael Moussa, and Ruth Lerman
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
Studies suggest that healthcare-affiliated populations are at an increased risk of experiencing chronic stress and burnout. Mindfulness meditation has become an established method to address and alleviate their effects, though it has not been extensively studied in the medical student population. The primary goals of this study are to assess the feasibility and efficacy of an 8-week, 30 contact hour MBSR course for first and second year medical students, and to assess its impact on their reported levels of stress, burnout, fear of compassion, and mindfulness. -

Urinary cytokines as potential biomarkers of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a pilot study
Nazia Saiyed, Ali Yilmaz, Sangeetha Vishweswariah, Sarah Bartolone, Tammy Osentoski, Stacey Ruff, Amita Pai, Michael Maddens, Khaled Imam, and Stewart F. Graham
Publication Date: 10-21-2022
-
HIV-associated nephropathy presenting as the first manifestation of HIV 2 infection
Kamil Sardarli, Rania Daboul Daboul, Sumesh Khanal, and Sami Zarouk
Publication Date: 4-2022
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.

