-

Effects of Comorbidities and Choice of Treatment on Overall Survival: A Beaumont Experience
Bilal M. Ali, Emma Herrman, James Huang Huang, and Mohammad Muhsin Chisti
Publication Date: 5-2023
First line therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is 7+3 regimen. It often cannot be used in elderly patients due to intensity. Venetoclax + hypomethylating agent (HMA) is approved for AML treatment in these patients. We investigate the efficacy of this treatment in a community setting where patients do not have the same resources available to them as a large academic center. Primary outcome was survival of patients greater than 60 years of age with a diagnosis of AML who received 7+3 therapy versus those who received venetoclax + HMA. Secondary outcomes included characteristics of those who received the two therapies.
-
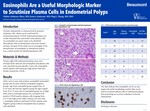
Eosinophils Are a Useful Morphologic Marker to Scrutinize Plasma Cells in Endometrial Polyps
Olabisi Afolayan-Oloye, Jessica Anderson, and Ping L. Zhang
Publication Date: 9-2022
Chronic endometritis is characterized by presence of plasma cells, which can be confirmed by immunostaining for CD138. Endometrial polyps can irritate endometrium and harbor some plasma cells. As eosinophils are much easier to be identified than plasma cells on hematoxylin and eosin stained sections, the goal of this study was to investigate if the identification of eosinophils in endometrial polyps was a useful marker for identifying plasma cells.
-
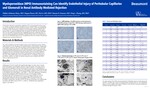
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Immunostaining Can Identify Endothelial Injury of Peritubular Capillaries and Glomeruli in Renal Antibody Mediated Rejection
Olabisi Afolayan-Oloye, Megan Moore, Wei Li, Hassan D. Kanaan, and Ping I. Zhang
Publication Date: 3-2022
-

CD30 Expression in Cutaneous B-Cell Lymphomas
Olabisi Afolayan-Oloye, Lili Zhao, Trilokraj Tejasvi, May P. Chan, Paul W. Harms, Douglas R. Fullen, Ryan A. Wilcox, and Alexandra C. Hristov
Publication Date: 10-2022
CD30 expression has been infrequently described in cutaneous B-cell lymphomas (CBCL). We examined CD30 expression in reactive lymphoid hyperplasia (RLH) and CBCL and correlated expression with clinicopathologic features.
-
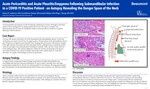
Acute Pericarditis and Acute Pleuritis/Empyema Following Submandibular Infection in a COVID-19 Positive Patient - an Autopsy Revealing the Danger Space of the Neck
Jessica D. Anderson, Seyedalireza Fatemi, Joseph Fullmer, and Ping I. Zhang
Publication Date: 10-2022
Acute pericarditis and empyema are life-threatening complications of severe odontogenic infections; reports of these findings from an autopsy perspective are rare. We report an autopsy case demonstrating infection from the mandibular molars to the pericardium and pleura in a patient following Covid-19 infection
-

Varieties of Renal Diseases Identified in Renal Biopsies of Patients Infected by COVID-19
Jessica D. Anderson, Wei Li, Hassan D. Kanaan, and Ping L. Zhang
Publication Date: 10-10-2022
COVID-19 has been shown to cause renal pathology by multiple proposed mechanisms. However, studies evaluating renal biopsies for the effects of COVID-19 remain limited. We report our experience in variety of renal pathologic diagnoses caused by COVID-19 infection in our health system.
-

Spectrum of C3 glomerulopathies (C3GNs) – single center experience
Mustafa M. Deebajah, Wei Li, Hassan Kanaan, and Ping L. Zhang
Publication Date: 10-10-2022
C3GNs represent a rare type of glomerulopathy due to the activation of alternative complement pathway, including C3 dominant glomerulonephritis (C3D-GN) and dense deposit disease (DDD). The goal of this study was to demonstrate a spectrum of C3GNs.
-

IgG4-Related Interstitial Nephritis (IRIN) Ranges from Kidney Mass to Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
Mai Elzieny, Wei Li, Hassan D. Kanaan, and Ping L. Zhang
Publication Date: 10-2022
IRIN can present as either renal mass or with AKI. The goal of the study was to present our 4 IRIN cases with different clinical scenarios.
-
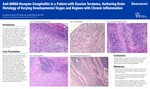
Anti-NMDA-Receptor Encephalitis in a Patient with Ovarian Teratoma, Harboring Brain Histology of Varying Developmental Stages
Seyedalireza Fatemi, Elaine Qu, and Joseph Fullmer
Publication Date: 6-2022
Anti-NMDA-receptor encephalitis is a subacute, autoimmune disorder thought to be caused by autoantibodies directed against the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. Although NMDAR encephalitis is a familiar entity to psychiatrists and neurologists, it is less commonly reported in the pathology literature. Clinical symptoms of anti-NMDAR encephalitis may mimic schizophrenia and psychotic spectrum disorders or substance-induced psychosis. Although initially described in association with ovarian teratomas in women, anti-NMDAR encephalitis has been reported in individuals without paraneoplastic association, as well as in males. Previous literature has suggested NMDA receptor expressing teratoma neurons are densely aggregated and are smaller in size. Ki-67 index can be higher in these neurons and they usually show B-cell lymphocytic infiltration around them. Herein, we report a case of a 29-year-old woman with suicidal ideation and other neuropsychiatric manifestations who was found to have a right ovarian cystic mass by imaging study. Microscopically, the resected ovarian mass is composed of mature skin, fat, cartilage and neural tissues. Nerve, ganglions and multiple brain tissues are present. Interestingly, cerebellum including external granular cell layer (normally only seen in infants), cerebrum-like, choroid plexus and other neural elements are present. There is peripheral lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates around and within the neuroglial matrix. Cerebral spinal fluid tested positive for Anti-NMDAR. The combined clinical, histological, and laboratory findings confirmed the above diagnosis. Its resultant relationship to cystic teratoma warrants awareness of this condition by pathologists. Although slow to respond to treatment, this patient now continues to show improvement with plasmaphoresis. Portions of this abstract have been previously presented at the ASCP meeting in 2021.
-
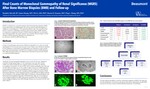
Final Counts of Monoclonal Gammopathy of Renal Significance (MGRS) after Bone Marrow Biopsies (BMB) and Follow-up
Brandon Metcalf, James Zhiyan Huang, Wei Li, Hassan D. Kanaan, and Ping L. Zhang
Publication Date: 3-21-2022
Background: MGRS is a relatively new concept for patients with renal paraprotein deposition (RPD) (except monoclonal cast nephropathy) with no bone marrow confirmed diagnosis of malignancy or premalignancy (< 10% monoclonal plasma cells). This concept has been used as a reason for a nephrology consult for a bone marrow biopsy (BMB), therefore it is important to evaluate the outcome of MGRS tentatively diagnosed via renal biopsy and confirmed by BMB. This study’s purpose was to identify what percentage of various subtypes of MGRS tentatively diagnosed via renal biopsy can be confirmed as MGRS by BMB and followup. Design: In total, 124 renal biopsies with variants of RPD were identified at our center out of 3811 renal biopsies (3.3% of overall cases) over past 10 years. Biopsy cases with known Myeloma, B Cell Lymphoma or Monoclonal Cast Nephropathy were separated as a heavy burden group. The remaining biopsies with RPD were considered as tentative MGRS diagnoses. Their BMB and clinical indices were followed up to determine the percent that resulted in a confirmed MGRS diagnosis. Results: Among the 124 renal paraprotein deposition cases, 43 cases (34.7%) were categorized to the heavy burden group (Figure). The remaining 81 cases with other variants of RPD were further divided into four categories based on the follow-up. Myeloma or Lymphoma were found in 34 cases (27.4%). Twelve outside consultation cases (10%) did not show follow-up biopsies as we were unable to obtain record access. BMB’s diagnosed as nonmalignant (6 cases, 4.8%) or premalignant (29 cases, 23.4%) were confirmed to be MGRS for a total of 35 cases (28.2%). Among the different categories of tentative MGRS, Monoclonal Light/Heavy Chain Deposition Diseases (L/HCDD) had the highest positivity rate for myeloma on the subsequent BMB. Proliferative Glomerulonephritis with Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Deposition (PGNMID) had a high rate of nonmalignant or premalignant diagnosis by BMB. Monoclonal Amyloidosis had some nonmalignant and pre-malignant diagnoses after BMB although myeloma was associated with this renal entity. Conclusions: The data indicate that BMB is crucial for confirming a diagnosis of MGRS. The study also provides pathologists and clinicians with general expectations regarding the possible BMB outcome for the many variants of MGRS identified tentatively via renal biopsy.
-
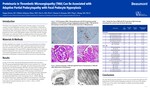
Proteinuria in Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA) Can Be Associated with Adaptive Partial Podocytopathy with Focal Podocyte Hyperplasia
Megan Moore; Olabisi Afaolayan-Oloye,; Wei Li; Hassan D. Kanaan; and Ping L. Zhang
Publication Date: 3-23-2022
Background: TMA associated renal failure is easy to understand, but it has been difficult to explain the significant proteinuria in some cases of TMA. We recently confirmed that 100% of hyperplastic podocytes in collapsing glomerulopathy stained positively for CD133 (a stem cell/progenitor marker) as previously reported. The goal of this study was to determine if there was significant fusion of foot processes (FFP) and CD133-positive hyperplastic podocytes in TMA to correlate with the proteinuria. Design: The study included 12 negative controls (renal parenchyma away from renal cell carcinoma) and 25 TMA cases, either induced by drugs or due to other etiologies (preeclampsia, TTP, atypical HUS, malignant hypertension, etc). The percentage of FFP was estimated and proteinuria levels were obtained for TMA cases. Both groups of cases were stained for CD133 by immunohistochemical methods and the # of glomeruli with CD133-positive hyperplastic podocytes was analyzed. Results: In total, 19 of 25 TMA cases had elevated protein/creatinine ratio more than 2 (Table). The TMA group had significantly higher levels of serum creatinine (2.81 ± 0.40 mg/dl) than the control group (0.95 ± 0.12 mg/dl). All controls showed positive CD133 staining only in the parietal epithelial cells (PEC), but none of them revealed positive CD133 staining in podocytes. In addition to positive CD133 staining in the PEC, 19 of 25 (76%) TMA cases showed positive CD133 staining in small clusters of hyperplastic podocytes within Bowman’s space (Figure, orange arrows in B and D). The average percentage of glomeruli with CD133-positive hyperplastic podocytes was 12 % in the TMA group. This was significantly higher than in the control group (0 %) (p = 0.0002), although this positivity did not show significant correlation with proteinuria in TMA group (r = 0.30, p = 0.1537). The percent of FFP (56 ± 4 %) was significantly correlated with proteinuria (protein/creatinine ratio 4.4 ± 0.6) (r = 0.46, p = 0.0237) in the TMA group. Conclusions: Our data indicate that the proteinuria in TMA can be associated with significant FFP. Small clusters of CD133- positive hyperplastic podocytes can be seen in the majority of TMA cases of this cohort, which supports an adaptive partial podocytopathy in some TMA cases.
-

Identification of Aggressive Variants of Mantle Cell Lymphoma Based on Flow Cytometry
Alan Nguyen, Alia Gupta, Marc Smith, and James Huang
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a rare subtype of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma characterized by a (1,14) translocation resulting in overexpression of cyclin D1.1 MCL variants and a heterogenous disease presentation make this a challenging diagnosis with a highly variable outcome. Pleomorphic and blastic variants have an aggressive clinical course and shorter survival than the classical type.2 The pleomorphic variant shows a marked variation in nuclear size, shape, and mitotic index.3 The blastic variant appears small and immature with fine chromatin mimicking acute leukemia.3 The aim of our study is to explore if flow cytometry analysis can help with the identification of aggressive MCL variants. -
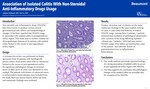
Association of Isolated Colitis With Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Usage
Ashbita Pokharel and Wei Li
Publication Date: 10-2022
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have been known to produce various clinical gastrointestinal side-effects and histopathological changes. It has been reported that NSAIDs usage is associated with isolated colitis in periappendiceal orifice region. This study aims to further evaluate the clinicopathologic features of 16 patients with isolated colitis limited to the cecum or peri-appendiceal orifice region.
-
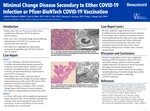
Minimal Change Disease Secondary to Either COVID-19 Infection or Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccination.
Ashbita Pokharel, Wei Li, Hassan D. Kanaan, Ping L. Zhang, and Neal B. Blatt
Publication Date: 9-2022
Introduction/Objective
Kidney injury has now become one of the known complications following COVID-19 infection and vaccination. Only few cases of minimal change disease following administration of COVID-19 vaccination and infection have been reported. This study was to highlight incidence of minimal change disease following COVID-19 infection or vaccination. Methods/Case Report
Case 1:15 year-old female with past medical history of asthma and hypercholesterolemia presented for evaluation of periorbital edema, nephrotic-range proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, elevated serum creatinine, elevated blood pressures, and hematuria after COVID-19 infection. Renal biopsy after 1 week of infection showed unremarkable glomeruli and negative immunofluorescent stains in glomeruli, and 20-30% fusion of foot processes. The biopsy was consistent with a minimal change disease with features of natural remission (her nephrotic-range proteinuria resolved soon after). Case 2: 18 year-old female with no significant past medical history presented with a chief complaint of generalized swelling, which started around the same time she received her 1st dose of Pfizer COVID vaccine (the 2nd dose 2 months later). She had a nephrotic range proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia, but normal level of serum creatinine. A renal biopsy after 4 months of vaccination showed unremarkable glomeruli by light microscopy, negative immunofluorescent study, but diffuse effacement of foot processes involving more than 80% of the examined loops by electron microscopy. This biopsy findings were consistent with a minimal change disease. Both patients did not receive any treatment before the renal biopsies. Results (if a Case Study enter NA)
NA Conclusion
Minimal change disease can be a rare complication following COVID-19 infection or Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination, raising a question if there are similar antigens induced by the infection or by the vaccination that trigger the minimal change disease. Further studies are needed to determine the incidence and pathophysiology of minimal change disease either post COVID-19 vaccines or following COVID-19 infections.
-
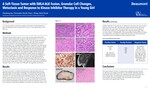
A Soft Tissue Tumor with EML4-ALK Fusion, Granular Cell Changes, Metastasis, and Response to Kinase Inhibitor Therapy in a Young Girl
Zhenhong Qu, Chris Hysell, Ping L. Zhang, and Mark Micale
Publication Date: 3-22-2022
Background: An increasing number of soft tissue neoplasms with fusion of well-defined driver genes are being discovered. We report such a case in a 3-year-old girl with a 2-year follow-up. Design: The patient first presented at age of 3.5 years with a painless right axillary/chest wall mass without constitutional symptoms. MRI demonstrated a 4.5 x 3.5 x 3.5 cm T2 hyper- and T1 hypointense mass. The mass was excised and showed a well-demarcated solid lesion with a homogeneous pale-white fleshy cut surface. No necrosis, myxoid or cystic change, hemorrhage, or calcification was noted. Microscopically, it was a variably hypercellular lesion composed of two main distinct cell types: oval fibroblast-like cells arranged in sheets with focal transition to spindle cells in whirling or storiform, and ganglion-like cells with abundant pale granular cytoplasm singly or in small clusters scattered among the fibroblast-like cells (Figure-1). Fibroblast-like cells contained a single resinoid nucleus with an irregular nuclear membrane surrounded by variable amount of eosinophilic cytoplasm with indistinct cell borders. Focal nuclear clustering and molding were seen. Patchy mild lymphocytic infiltrate was noted. No nuclear pleomorphism, necrosis or mitotic figure was identified. Immunohistochemically, both types of tumor cells were diffusely positive for ALK, CD34 and TFE3 (Figure-2) but negative for most lineage markers (Table). Next-generation-sequencing revealed EML4-ALK gene fusion of 5 a/b variant. No NTRK gene rearrangement was detected. Results: The tumor recurred in 13 months with metastasis to regional lymph nodes and right lung. Biopsy showed similar morphology and immunohistochemical profile. Treatment with oral ALK inhibitor (crizotinib) was initiated at 200 mg BID. Seven weeks later, CT scan demonstrated partial radiological response with a measurable decrease in the main tumor size from 8.7 to 7.5 cm. The tumor regrew to 9.0 x 7.0 x 7.0 cm and became firm nine weeks thereafter crizotinib was inadvertently discontinued by her mother. Reinstituting the therapy led to second tumor reduction (to 8.7 x 5.4 x 6.4 cm) and tumor softening on palpation. The patient is currently alive, active, and stable without any constitutional symptoms. Conclusions: This tumor’s features of EML4-ALK gene fusion, distinct innocuous histology, but rapid growth and metastasis, and response to ALK inhibitor add to the pathological and clinical spectrum of the kinase fusion-positive soft tissue neoplasms.
-

CSF Flow Cytometry in Patients with Leukemia and Lymphoma
Patricia Rusli and James Huang
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
The use of flow cytometric testing in analyzing bodily fluid for hematologic neoplasms is not novel. Flow cytometric immunophenotyping of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has previously been demonstrated to have high sensitivity and specificity for the detection of lymphoma and leukemia. They are able to determine definitive diagnostic information from even very low cellularity samples. In this study, we reviewed the experience of our clinical flow cytometry laboratory in evaluating CSF specimens in order to find the disease distribution of positive CSF samples. -
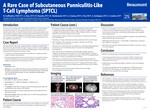
A Rare Case of Subcutaneous Panniculitis-Like T-cell Lymphoma
Blake Seelbinder, Angela Kim, Marcos Rosado, Mohamed Musheinesh, Amanda Cimino, John Pui, Armen Korkigian, and Craig Gordon
Publication Date: 5-2022
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTCL) is a rare and typically slow growing variant of T-cell lymphoma. The clinical course usually mimics infectious panniculitis. It characteristically affects the subcutaneous adipose tissue of the trunk or extremities without resultant lymph node involvement. It comprises
-
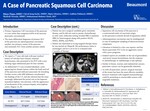
A Case of Pancreatic Squamous Cell Cancer
Bijaya Thapa, Ujjwal Jung Karki, Bipin Ghimire, Ashbita Pokharel, Shailesh Niroula, and Mohammad Muhsin Chisti
Publication Date: 10-2022
Introduction
Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the pancreas is a rare entity that comprises 0.05% of all exocrine pancreatic carcinomas. The main differential diagnoses of primary SCC of the pancreas are adenosquamous carcinoma- another rare primary tumor of the pancreas and metastatic SCC from another primary site.
Discussion
Squamous cell carcinoma of the pancreas is a controversial entity of uncertain origin, as the pancreas is entirely devoid of squamous cells[1] • Adenosquamous carcinomas may be misdiagnosed in case of inadequate sampling of adenocarcinoma component. • Literature is limited to a few case reports, and has shown pancreatic SCC to be an aggressive cancer with a poor prognosis. • Isolated reports are available on the use of gemcitabine and newer taxane formulations, but the response to chemotherapy or radiotherapy is sub-optimal. • Similar to breast, ovarian, and endometrial cancers; pancreatic cancers can be genetically inherited. • As with all pancreatic cancers, surgical resection of the tumor has been the most effective modality, however treatment with targeted immunotherapy could be promising in unresectable tumors with targetable mutations.
-

Characterization of the Clinical Impact of a Celiac Disease Algorithm on Diagnostic Workup of Patients at Beaumont Hospital Royal Oak
Omid Vadpey and Gabriel N. Maine
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
Advancements in medical technology and laboratory testing have prompted room for more accurate diagnostic procedures that can aid in diagnostic efficiency, reducing time to diagnosis, unnecessary test ordering, and costs. Celiac Disease is a complex gastrointestinal autoimmune disorder characterized by symptoms that mimic other bowel diseases, such as diarrhea, steatorrhea, and malnutrition. The primary goal of this pilot study is to determine if the implementation of a diagnostic serologic algorithm differs from the current standard of practice for patients that are suspected of celiac disease at Beaumont Health-Royal Oak (BH-RO). -

Characterization of CD57+ T-cell subset in Blood, Bone Marrow, and Lymphoid Tissue
Michelle Ka Yan Wu, Xia Chen, and James Huang
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
A CD57+ T-cell subset has shown to have diagnostic and prognostic significances in some cancers. However, its specific distributions in tissues and specific variations among different diseases are yet to be further defined. This Embark project aims to examine the distributions and antigen expression profiles in the CD57+ T-cell subset in peripheral blood (PB), bone marrow (BM), and lymph node (LN).
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.

