-
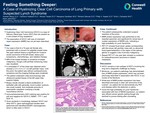
Feeling Something Deeper: A Case of Hyalinizing Clear Cell Carcinoma of Lung Primary With Suspected Lynch Syndrome
Hussein Bazzy, Cameron Hubbard, Ahmad Tahawi, Narayana Gandham, Richard Zekman, Phillip V. Kaplan, Erich J. Schwartz, and Kevin Jamil
Publication Date: 5-22-2024
Hyalinizing Clear Cell Carcinoma (HCCC) is a type of Salivary Gland-type Tumor (SGT) that can present as a rare subset of lung neoplasms1
The association of HCCC with loss of mismatch repair expression (MMR) has not yet been described.
-
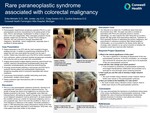
Rare paraneoplastic syndrome associated with colorectal malignancy
Erika Michelin, Jordan Jay, Craig Gordon, and Cynthia Sandona
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Paraneoplastic hypertrichosis lanuginosa acquisita (PHLA) is a rare paraneoplastic syndrome characterized by the global growth of fine hairs. PHLA’s dermatologic manifestation is similar to languo hair which is thin and unpigmented. Other associated symptoms include glossitis, weight loss and diarrhea. Though PHLA's etiology is unknown, this rare syndrome is strongly associated with malignancy. Specifically, colonic malignancies, especially when it manifests in female patients.
-

Effect of Comorbidities and Choice of Treatment on Overall Survival in Elderly Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Beaumont Experience
Bilal M. Ali, Emma Herrman, James Huang Huang, and Mohammad Muhsin Chisti
Publication Date: 5-2023
First line therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is 7+3 regimen. It often cannot be used in elderly patients due to intensity. Venetoclax + hypomethylating agent (HMA) is approved for AML treatment in these patients. We investigate the efficacy of this treatment in a community setting where patients do not have the same resources available to them as a large academic center. Primary outcome was survival of patients greater than 60 years of age with a diagnosis of AML who received 7+3 therapy versus those who received venetoclax + HMA. Secondary outcomes included characteristics of those who received the two therapies.
-

Outcomes of DA R-EPOCH versus R-CHOP in treating patients diagnosed with Double-Expressor lymphoma
Phat Duong and Ishmael Jaiyesimi
Publication Date: 5-2023
Double-expressor lymphoma (DEL) is a subtype of Diffuse Large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) that is associated with poor prognosis. The standard treatment for DLBCL is rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP). It is hypothesized that the aggressive nature of DEL deserves a more intense regimen such as dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin plus rituximab (DA-R-EPOCH). A comparison of outcomes between those two treatments is needed to guide clinical decisions.
-

Demographics and Survival in AML patients over 60 Years of Age. A Single Institutional Analysi
Damilola Gbadebo, Nwabundo Anusim, and Ishmael Jaiyesimi
Publication Date: 5-2023
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is a malignancy of the myeloid cell line. Patients diagnosed with AML, typically exhibit symptoms of neutropenia, anemia and thrombocytopenia. The diagnosis of AML is based on greater than 20 percent of myeloid cells in the bone marrow (1). Some risk factors for acquiring the disease include, but not limited to age, sex, smoking, exposure to certain chemicals, radiation, genetic predisposition and being treated with certain chemotherapeutic agents (2).
AML is frequently diagnosed among people between ages 65-74, with a current relative survival rate for AML being 28.7%. Men account for majority of these cases, at a rate of 5.2 per 100,000 persons compared to 3.6 per 100,000 persons for female patients (3).
Our study will assess whether treatment for AML patients has improved after 2015 with the utilization of novel chemotherapeutic agents, particularly for Beaumont Hospital patients. -

Comparing overall survival outcomes of patients treated with immunotherapy + chemotherapy, or chemotherapy + radiation for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Sukhmani Singh and Ishmael Jaiyesimi
Publication Date: 5-2023
Traditionally, non-small cell lung cancer has been treated with chemotherapy or surgery, and remained first line treatment until around 2015 when PDL-1 immune checkpoint immunotherapy was introduced and for many patients where it become the standard first line treatment. A few research studies comparing outcome differences between patients receiving immunotherapy versus patients who did primarily chemotherapy as first line treatment indicate increased survival benefit, however, as immunotherapy is still relatively new, longer term survival benefit and analysis of other factors is continuing to be delineated.
-

Dietary supplement use among BRCA1/2 mutation carriers
Ryan Rogers, Tara Ramgarajan, Virginia Uhley, Kristina Ivan, and Dana Zakalik
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
Women who carry BRCA1/2 mutations are at significantly increased risk of breast, ovarian, pancreatic and other cancer. Little is known regarding the use of dietary supplements among women harboring BRCA1/2 mutations. This study aims to characterize the utilization of and attitudes toward dietary supplement use in women who carry BRCA1/2 mutations. -
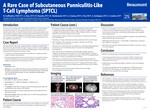
A Rare Case of Subcutaneous Panniculitis-Like T-cell Lymphoma
Blake Seelbinder, Angela Kim, Marcos Rosado, Mohamed Musheinesh, Amanda Cimino, John Pui, Armen Korkigian, and Craig Gordon
Publication Date: 5-2022
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTCL) is a rare and typically slow growing variant of T-cell lymphoma. The clinical course usually mimics infectious panniculitis. It characteristically affects the subcutaneous adipose tissue of the trunk or extremities without resultant lymph node involvement. It comprises
-
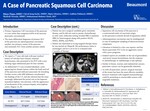
A Case of Pancreatic Squamous Cell Cancer
Bijaya Thapa, Ujjwal Jung Karki, Bipin Ghimire, Ashbita Pokharel, Shailesh Niroula, and Mohammad Muhsin Chisti
Publication Date: 10-2022
Introduction
Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the pancreas is a rare entity that comprises 0.05% of all exocrine pancreatic carcinomas. The main differential diagnoses of primary SCC of the pancreas are adenosquamous carcinoma- another rare primary tumor of the pancreas and metastatic SCC from another primary site.
Discussion
Squamous cell carcinoma of the pancreas is a controversial entity of uncertain origin, as the pancreas is entirely devoid of squamous cells[1] • Adenosquamous carcinomas may be misdiagnosed in case of inadequate sampling of adenocarcinoma component. • Literature is limited to a few case reports, and has shown pancreatic SCC to be an aggressive cancer with a poor prognosis. • Isolated reports are available on the use of gemcitabine and newer taxane formulations, but the response to chemotherapy or radiotherapy is sub-optimal. • Similar to breast, ovarian, and endometrial cancers; pancreatic cancers can be genetically inherited. • As with all pancreatic cancers, surgical resection of the tumor has been the most effective modality, however treatment with targeted immunotherapy could be promising in unresectable tumors with targetable mutations.
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.

