-

Repair of Achilles Tendon Re-Rupture with FHL Transfer: A Case Study
Taylor Allison and Joshua Kazdan
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
The Achilles tendon consists of the soleus muscle and two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle. Loss of its function can result in loss of plantarflexion strength, which can impact activities of daily living. In a study by Scheller et al, Achilles tendon ruptures were missed on initial evaluation on 25% of their patients. Other studies have reported a similar incidence of misdiagnoses. Patients may also delay treatment due to decreased pain after the initial injury. Ruptures diagnosed 4 weeks from injury are often considered chronic, and many of these patients benefit from surgical repair. A flexor hallucis longus (FHL) transfer may be utilized to augment an Achilles tendon repair, especially in cases with significant gapping. The following case utilizes the FHL tendon transfer in addition to open end-to-end repair using the Percutaneous Achilles Repair System (PARS) following a chronic Achilles tendon rupture with subsequent re-rupture after surgical repair.
-

Case Report of Bullous Diabeticorum: A self-limiting condition with potentially devastating consequences
Taylor Allison and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Bullous diabeticorum (BD) is a skin manifestation of patients with diabetes mellitus with an incidence of about 0.16% per year (Larsen et al) although the condition is believed to be widely underdiagnosed. The blistering disease favors acral regions of the body including the feet. There are no accepted diagnostic tests, and histopathology results are often inconclusive which makes BD a clinical diagnosis of exclusion. It is often self-limiting and resolves in a few weeks without residual sequelae. However, it may present with a secondary bacterial infection which can put patients at risk for soft tissue infections and osteomyelitis requiring more aggressive treatment.
▪ Bullous diabeticorum (BD) is a skin manifestation of patients with diabetes mellitus with an incidence of about 0.16% per year (Larsen et al) although the condition is believed to be widely underdiagnosed. The blistering disease favors acral regions of the body including the feet. There are no accepted diagnostic tests, and histopathology results are often inconclusive which makes BD a clinical diagnosis of exclusion. It is often self-limiting and resolves in a few weeks without residual sequelae. However, it may present with a secondary bacterial infection which can put patients at risk for soft tissue infections and osteomyelitis requiring more aggressive treatment.
-
Septic First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Arthrodesis with Alternative Mini-Rail Fixation
Brenna Barker, Morgan Gascoyne, and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
For non-infection cases, first metatarsal phalangeal joint arthrodesis is a definitive procedure for painful, arthritic joints.
Standard fixation methods include screws, plates, staples, or a combination of the three.
For complex septic joint cases, an alternative method of fixation is needed to reduce the risk of infection retention.
-
Stepping Into Relief: Conquering Rheumatoid Arthritic Foot Pain with Podiatric Management
Natalie Diaz, Marshall Solomon, and Inocencio Cuesta
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic multifactorial autoimmune disease that causes progressive joint destruction along with causing cutaneous manifestations such as nodules. RA negatively impacts life by producing pain, impairing quality of life and biomechanical function of the lower extremities.
-

Complications and Formation of Sinus Tracts Due to Presence of Lead From Foreign Bodies in Soft Tissue: A Case Report
Peter J. Godoy and Marshall G. Solomon
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
A cornerstone of lower extremity limb salvage is to avoid development of wound complications involved in soft tissue infections . Predicting probability of sinus tract development due to presence of lead in soft tissues from foreign bodies. In this particular case a bullet fragment from a previous gunshot wound was noted to be the catalyst disrupting multiple biologic processes and impairing the function of soft tissues to heal. Predicting a level of contamination in this particular case lead believed to cause oxidative stress and inflammation and prompt excisional removal can avoid sinus tract formations and complications. This study presents a unique case that demonstrates beneficial patient care when a initial suspicion for wound contamination via lead and Swift intervention can lower probability of complications of wound healing.
-

Cohort Study Using a Survey to Evaluate the Effects of Sleep on Hba1c Levels and Foot Pathology in Patients Seen in the Podiatry Clinic
Carmen Johnson, Eric Li, Jihan Toma, and Marshall G. Solomon
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
We investigate the impacts of sleep issues on patients in the podiatry clinic by comparing HbA1c, sleep, and foot pathology. Diabetic foot pathology of peripheral arterial disease, peripheral neuropathy, lower extremity ulcerations, and a history of lower extremity amputation all increase the patient's risk of future amputation. Once a patient has an amputation of the lower extremity the five-year mortality rates are 40-70%. So, limb salvage not only improves the quality of life, but also increases the life expectancy for patients. Through a survey and chart review, we are investigating possible impacts of sleep issues on diabetic patients seen in the podiatry clinic as it relates to limb salvage
-

The Diagnosis of Polyarteritis Nodosa in the Setting of Lower Extremity Lesions: A Case Report
Eric Li, Jihan Toma, and George Gopoian
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is a systemic necrotizing vasculitis affecting medium-sized arteries, involving multiple organs, with the most frequently affected tissues being skin and peripheral nerves (1). The distinct pearl neckless pattern led to the naming of this condition (2). Cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa (CPAN) is a variant of PAN confined to the skin, muscles and peripheral nerves in the absence of any systemic involvement (1). This rare form of systemic necrotizing vasculitis is limited to the medium-sized arteries of the skin and has a more favorable prognosis (1). PAN is also linked to Hepatitis B(2). The current diagnostic criteria for CPAN were proposed in 2009 by Nakamura et al.and include the presence of cutaneous manifestations and biopsy-proven fibrinoid necrotizing vasculitis of small and medium sized arteries (1). General non-specific symptoms such asthenia, fever, weight loss, myalgia, and arthralgia are frequently the symptoms of PAN (1). Neurological manifestation occur in more than 2/3 of patients, more commonly as motor and sensory mononeuritis multiplex of the peripheral nerves (1). Peripheral neuropathy is typically distal, asymmetric, and can be rapid-onset, often associated with localized skin edema (1). Skin lesions, including nodules, purpura, necrotic ulcers, and livedo reticularis, are present in half of the patients (1). In cases of cutaneous manifestations suggestive of vasculitis, a skin biopsy is recommended (1). The biopsy should be deep enough to include the dermal layer where medium-sized arteries are located (1). A subset of PAN, known as cutaneous PAN (CPAN) is confined to the skin and requires different management (1).
-

The Curious Case of Ainhum Dactolysis Spontanea
Jesse Miller, Michele Bertele-Semma, and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
46 yo African male, no major PMH.
Pt presents with severe pain in the right 5th toe.
Pt had used a corn remover at home treatment 2 years ago which they stated started the progression in the pain of the patient.
Pt states that the toe has progressively become more constricted and painful.
Pt states that they want their toe amputated to relieve the pain.
-
Diabetic Limb Salvage: Chopart Amputation
Jesse Miller and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Diabetic limb salvage is the act of saving a limb, even with decreased function after infection.
It is the difficult choice of the surgeon/patient to decide to proceed with salvage versus amputation proximally.
-

Case Report of Surgical Management for Charcot Foot Medial Column Beaming with STJ Arthrodesis
Prachi Patel and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Medial column beaming is a surgical procedure that involves inserting a metallic beam to the medial column of the foot to treat the Charcot deformity of the foot.
A surgeon will use a large diameter screw to insert a beam into medial column which includes the first metatarsal, medial cuneiform, navicular and talus (fig 3) The beam shares the load of weightbearing with the foot's ligaments and joints, reducing the abnormal loss of structural integrity that can occur in Charcot arthropathy of the foot.
Subtalar joint fusion is often performed concurrently with medial column beaming to enhance the overall stability of the foot. This combined approach aims to stabilize the foot, correct deformities, and prevent further progression of the disease, which are critical for enhancing functional outcomes of the foot.
-
Failed Medial Column Fusion due to Subtalar Joint Instability
Travis Rich, Randy Semma, and Michele Bertelle-Semma
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
CNA is a destructive complication affecting the bone and joint structure, most often in diabetics w/ longstanding peripheral neuropathy.
High incidence of major amputation associated with Charcot foot.
-

Antibiotics Vs Surgical Resection in Foot and Ankle Osteomyelitis
Travis Rich and Marshall G. Solomon
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Osteomyelitis, a serious bone infection, is particularly challenging in diabetic patients due to poor vascularization and impaired immune response.1 Timely and effective treatment is essential to prevent severe complications, including limb loss or even death.2 This study aims to evaluate the likelihood of surgical excision or amputation versus antibiotic treatment alone in diabetic patients with bone biopsyconfirmed acute osteomyelitis of the lower extremity.
-

Sole Searching: The Mystery of a Left Foot Mood Swing Unraveled
Kaitlin Sebranek and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
About 0.2% of patients in the Diabetic population have Charcot Neuroarthropathy.
When the gold standard of offloading in a total contact cast fails for CN patients, surgical treatment can be considered to achieve a stable, plantigrade, and functional foot.
Due to the complexity of the condition, potential complications such as hardware breakage, nonunion, and infection can result over time.
-
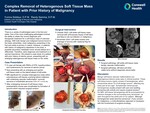
Complex Removal of Heterogenous Soft Tissue Mass in Patient with Prior History of Malignancy
Yumna Siddiqui and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
There is a variety of pathologies seen in the foot and ankle. One of the more challenging pathologies involves the ability to obtain the correct diagnosis and therapeutic treatment for a soft tissue mass of unknown etiology. With both benign and malignant tumors found in the lower extremities, most malignancy presenting in the foot and ankle is primary in nature. However, in patients with history of malignancy elsewhere in the body, a possible secondary metastatic tumor should always be a differential. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment is of upmost importance. We present a case study of a patient with prior history of uterine cancer, presenting with an enlarging heterogenous soft tissue mass on her ankle.
-
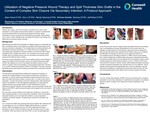
Utilization of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy and Split Thickness Skin Grafts in the Context of Complex Skin Closure Via Secondary Intention: A Protocol Approach
Jihan Toma, Eric Li, Randy Semma, Michele Bertelle-Semma, and Asif Khan
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Patients with complex, chronic foot wounds or ulcerations are at risk for major amputations. In this quality improvement (QI) initiative, we present an implemented protocol for patients with foot ulcerations and attempt to heal them using a combination of wound vac therapy and split thickness skin grafting. These patients have a history of either diabetes and/or neuropathy that makes wound healing more difficult than an otherwise healthy individual.
-
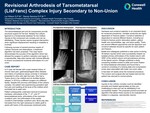
Revisional Arthrodesis of Tarsometatarsal (LisFranc) Complex Injury Secondary to Non-Union
Lei Wilson and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
The tarsometatarsal joint and its components provide structural support for the foot. Notably the Lisfranc ligament is a fundamental stabilizer for the midfoot. Injuries to this component are complex and can be debilitating. These injuries require surgical intervention when significant displacement resulting in instability is involved.
Following success of several previous repairs of Lisfranc fractures and dislocations, a treatment algorithm has been proposed. This case report demonstrates the success of the algorithm which has allowed the surgeon to perform reduction and repair in a reproducible, step-wise manner with minimal difficulty to ensure successional revisional arthrodesis of a non-union
-

Case Report of Bullous Diabeticorum: A self-limiting condition with potentially devastating consequences
Taylor Allison and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
Bullous diabeticorum (BD) is a skin manifestation of patients with diabetes mellitus with an incidence of about 0.16% per year (Larsen et al) although the condition is believed to be widely underdiagnosed. The blistering disease favors acral regions of the body including the feet. There are no accepted diagnostic tests, and histopathology results are often inconclusive which makes BD a clinical diagnosis of exclusion. It is often self-limiting and resolves in a few weeks without residual sequelae. However, it may present with a secondary bacterial infection which can put patients at risk for soft tissue infections and osteomyelitis requiring more aggressive treatment.
-
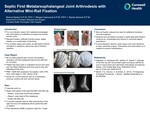
Septic First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Arthrodesis with Alternative Mini-Rail Fixation
Brenna Barker, Morgan Gascoyne, and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
For non-infection cases, first metatarsal phalangeal joint arthrodesis is a definitive procedure for painful, arthritic joints.
Standard fixation methods include screws, plates, staples, or a combination of the three.
For complex septic joint cases, an alternative method of fixation is needed to reduce the risk of infection retention.
-

Cohort Study Using a Survey to Evaluate the Effects of Sleep on Hba1c Levels and Foot Pathology in Patients Seen in the Podiatry Clinic
Carmen Johnson, Eric Li, Jihan Toma, and Marshall G. Solomon
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
We investigate the impacts of sleep issues on patients in the podiatry clinic by comparing HbA1c, sleep, and foot pathology. Diabetic foot pathology of peripheral arterial disease, peripheral neuropathy, lower extremity ulcerations, and a history of lower extremity amputation all increase the patient's risk of future amputation. Once a patient has an amputation of the lower extremity the five-year mortality rates are 40-70%. So, limb salvage not only improves the quality of life, but also increases the life expectancy for patients. Through a survey and chart review, we are investigating possible impacts of sleep issues on diabetic patients seen in the podiatry clinic as it relates to limb salvage.
-
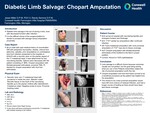
Diabetic Limb Salvage: Chopart Amputation
Jesse Miller and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
Diabetic limb salvage is the act of saving a limb, even with decreased function after infection.
It is the difficult choice of the surgeon/patient to decide to proceed with salvage versus amputation proximally.
-
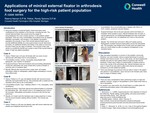
Applications of Minirail External Fixator in Arthrodesis Foot Surgery for the High-Risk Patient Population A Case Series
Reema Naman and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
Since the inception of external fixation, there have been many modifications to the utilization of the devices, including the size. The minirail external fixator has evolved since the usage for bracymetatarsia into more complex devices. In the podiatric patient population, there are many comorbidities encountered such as diabetes, idiopathic neuropathy, and smoking. In the diabetic neuropathic population the purpose of use of the minirail external fixator was to provide additional stability as a mini-superconstruct as per Sammarco principles. An additional benefit of the fixator is the option of removing the pins if there are any signs of infection. The purpose of this case series is to exhibit the benefit and myriad of uses of the minirail external fixator in high-risk patient population.
-
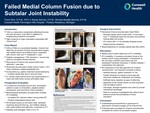
Failed Medial Column Fusion due to Subtalar Joint Instability
Travis Rich, Randy Semma, and Michele Bertelle-Semma
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
- CNA is a destructive complication affecting the bone and joint structure, most often in diabetics w/ longstanding peripheral neuropathy.
- High incidence of major amputation associated with Charcot foot
-
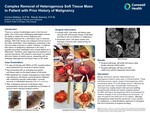
Complex Removal of Heterogenous Soft Tissue Mass in Patient with Prior History of Malignancy
Yumna Siddiqui and Randy Semma
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
There is a variety of pathologies seen in the foot and ankle. One of the more challenging pathologies involves the ability to obtain the correct diagnosis and therapeutic treatment for a soft tissue mass of unknown etiology. With both benign and malignant tumors found in the lower extremities, most malignancy presenting in the foot and ankle is primary in nature. However, in patients with history of malignancy elsewhere in the body, a possible secondary metastatic tumor should always be a differential. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment is of upmost importance. We present a case study of a patient with prior history of uterine cancer, presenting with an enlarging heterogenous soft tissue mass on her ankle.
-
Utilization of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy and Split Thickness Skin Grafts in the Context of Complex Skin Closure Via Secondary Intention: A Protocol Approach
Jihan Toma, Eric Li, Randy Semma, Michele L. Bertelle-Semma, and Asif Khan
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
Patients with complex, chronic foot wounds or ulcerations are at risk for major amputations. In this quality improvement (QI) initiative, we present an implemented protocol for patients with foot ulcerations and attempt to heal them using a combination of wound vac therapy and split thickness skin grafting. These patients have a history of either diabetes and/or neuropathy that makes wound healing more difficult than an otherwise healthy individua
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.


