-

Case Report: Diagnosing & Treating Triple Negative Breast Cancer During Pregnancy
Sydney Mefford and Chloe Page
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Pregnancy associated breast cancer (PABC) is rare and can be seen in every 1 in 3000 pregnant patients. It is associated with a high morbidity rate, especially in cases of Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC).
Prevalence has increased as society grows to have pregnancies at later ages. Risk is elevated for 1 year after delivery of baby.
-
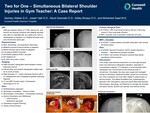
Two for One – Simultaneous Bilateral Shoulder Injuries in Gym Teacher: A Case Report
Zachary Walker, Josiah Valk, David Sosnoski, Kelley Brossy, and Mohamed Saad
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
28M gym teacher history of T1DM, seizure d/o, and alcohol use disorder presents with bilateral shoulder pain after an inebriated fall, two nights prior. Not on antiepileptics at baseline. C/o bilateral shoulder pain and mid-thoracic spine pain.
-

Effects of Education on Gardasil Administration Within Varying Patient Demographics
Emily Zajac, Megan Amos, Farrar Jean Ford, Kelly Dubay, Teresa Mccartney, and Chen Shen
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
The purpose of this quality improvement study is to evaluate how physician education impacts patient education and HPV vaccination rates within obstetric and gynecologic clinics affiliated with Corewell Health Farmington Hills Hospital, with the purpose of improving HPV vaccination rates among women. Patient demographics and incidence of physician education will be analyzed for the relationship to HPV vaccination rates within the three OBGYN clinics.
Current data indicates that this quality improvement measure is needed for the population seen by these clinics. According to MCIR, a small percentage of teenage patients in Michigan have completed the 3 dose HPV vaccination series (16.7% for males and 32.8% of females). Nationally, while HPV vaccination rates continues to increase, they remain lower than vaccination coverage with routinely recommended vaccines. Locally, Oakland county HPV vaccination rates remain lower than Michigan and national numbers.
OBGYN providers do not see the target population (11–12-year-olds) for the initial vaccine. Given that ACOG recommendations for vaccination have recently changed, we aim to increase provider knowledge of these recommendations and thus improve the vaccination rates. Provider education and recommendation for vaccines has been shown to correlate in favor of increased incidence of HPV vaccination.
Initial findings noted that after provider education and education to the patients, patients decided to review information on their own terms. Therefore, not showing a sudden increase in the vaccine rate.
-

The Effects of BMI on the Development of Radiation Cystitis Onset: A Pilot Study
Kelsa G. Kazyak and Bernadette MM Zwaans
Publication Date: 5-2023
Radiation cystitis (RC) is a debilitating adverse side effect of pelvic radiation therapy. Despite advancements within the field of radiation oncology, the location of the bladder makes it difficult to avoid during radiation and approximately 5-10% of cancer survivors with a history of pelvic radiation are at risk. While RC is not common, the long-term effects can be crippling and we hope to provide more information on the risk factors to help survivors and inform clinicians.
-

Gestational Weight Gain and the Associated Perinatal Outcomes in Middle Eastern Women
Dana Rector and Zeynep Alpay-Savasan
Publication Date: 5-2023
Gestational Weight Gain (GWG) can impact perinatal outcomes for mothers and infants, especially if the mother gains inadequate or excessive weight during pregnancy. We hypothesized that Middle Eastern women would be more likely to gain inadequate weight, compared to the general population, resulting in adverse perinatal outcomes.
-

Identifying Discrepancies in Diagnosis of PCOS with Use of Different Diagnostic Criteria
Naveena Daram and Sangeeeta Kaur
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. Two main diagnostic criteria are used for PCOS: the Rotterdam and Androgen Excess Society (AES) criteria. Depending on which criteria is used, the diagnosis of PCOS may change. Therefore, our study investigates the discrepancies in the diagnosis of PCOS when using the Rotterdam versus the AES scale in the Beaumont Health System. This is clinically significant because a PCOS diagnosis should not be made lightly as it can come with many lifelong social, emotional, and medical implications. -

COVID-19 is Associated with Early Emergence of Preeclampsia: Results from a Large Regional Collaborative
Theodore Jones, Sonia Sajja, and Ray Bahado-Singh
Publication Date: 2-4-2022
An increased risk of preeclampsia (RR=1.8), driven almost entirely by an increase in preterm preeclampsia (RR=2.85) was observed in COVID pregnancies (Table 1), with a dose-response relationship with symptomatology and severity (Table 2).
▪ The associations between COVID-19 disease and preeclampsia or preterm preeclampsia were independent of other risk factors, as demonstrated by the minimal changes in RR after adjustment for confounders (Table 1). However, African American (AA) COVID patients experienced preterm preeclampsia 1.9 times more than COVID patients of other races (10.1 vs 5.3), an increase not observed in control patients.
▪ The strength of the association for COVID with preeclampsia was comparable to the association of preeclampsia with chronic hypertension and nulliparity (data not shown).
▪ Increasing symptoms & severity of COVID-19 were associated with an increased risk for preeclampsia with placental lesions, even after adjustment for relevant covariates (Tables 1& 2).
▪ Non-Preeclamptic COVID patients had an increased trend of placental lesions compared to non-COVID patients, reaching significance for intravillous thrombin.
-

Racial disparities in risk for COVID-19 in pregnancy: Results from a large regional collaborative
Theodore Jones, Sonia Sajja, and Ray Bahado-Singh
Publication Date: 2-4-2022
- Though previous studies have looked at both COVID-19 outcomes in pregnancy and racial disparities among patients with COVID-19, few have specifically studied racial disparities among pregnant patients with COVID-19.
- Our goal in this study is to analyze the relationship, if any, between race and disparate COVID-19 risk in pregnancy.
-

Descriptive Causes for Decreased Breast and Cervical Screenings in Sikh Populations
Varneet Kaur Brar
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
Prior evaluations of breast and cervical cancer screens have found that immigrant South Asian women have lower compliance rates when compared to non-immigrant, white, or African American women (Shoemaker, 2016). It is widely accepted that early detection of cancers can improve outcomes for patients, and that screenings like mammography and pap smear tests are critical in this process. The aim of this study was to evaluate compliance rates for breast cervical cancer screens in Sikh women in Michigan, as well as to investigate attitudes which may be contributing to any disparities which may exist. -

VBAC Success in Women with Diabetes Mellitus Types I + II: A Pilot Study
Emma Randall, Rachel Taylor, Sarah Becker, and Zeynep Alpay-Savasan
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
Due to a rise in cesarean sections since the 1970s, the American College of Gynecology has acted to reduce unnecessary cesarean deliveries. In 2017, ACOG released clinical management guidelines for vaginal birth after cesarean delivery (VBAC), including a nomogram to predict VBAC success. This nomogram, developed by Grobman et al. (2007), explored factors impacting VBAC success for delivery at term for a singleton pregnancy. While the presence of diabetes was evaluated in the study, it was not found to be a significant factor in predicting outcome. This study will take a more detailed look at if pre-existing diabetes impacts a woman’s VBAC success.
-

Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification System- Teaching Residents with a 3D Model
Jaber Saad, Patricia Franz, and Kurt Wharton
Publication Date: 4-28-2022
Objectives
- Create and test the effectiveness of a simple model to teach POP-Q to current Ob/Gyn residents at Beaumont Health - Roya Oak
- We hope to gain medical education knowledge to best guide future efforts to teach this material
-- Secondarily, we surveyed recent graduates to examine their utilization of POP-Q and hope to inspire future research that will examine if using 3D model to teach POP-Q will make residents more likely to incorporate it in their practice as attendings.
-

Population-based Evaluation of Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome in Southeast Michigan
Alia Ahmed Shah, Linnea Nierenberg, and Zeynep Alpay Savasan
Publication Date: 4-28-2022
Objectives
- To identify the distribution of NaS in patients with opioid abuse in Beaumont Health System
- To identify characteristics of these pregnant patients in our health system.
-

cfDNA in maternal blood and artificial intelligence: accurate prenatal detection of fetal congenital heart defects
Sangeetha Vishweswaraiah, Perry Friedman, Ciara Talbot, Buket Aydas, Siddesh Southekal, Nitish K. Mishra, Chittibabu Guda, Ali Yilmaz, Uppala Radhakrishna, and Ray Bahado-Singh
Publication Date: 10-21-2022
-

Effectiveness of Prenatal Screening Tests on Predicting Cardiac Anomalies
Stephanie Y. Wong and Zeynep Alpay Savasan
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the leading cause of birth defect-associated infant death. With 1 in 111 newborns born with CHD and an elevated infant mortality rate of 30-50%, early detection is imperative. Current prenatal screening mainly focuses on detecting chromosomal anomalies. However, the accuracy of these exams on detecting fetal cardiac abnormalities is not well researched. The primary goal of this study is to compare three prenatal screening tests’ potential, i.e anatomy ultrasound, nuchal translucency (NT), and cell-free DNA (cfDNA), in identifying risk for fetal cardiac anomalies. -

Longitudinal metabolomics in the brain of mouse models with mild and severe traumatic brain injury
Ali Yilmaz, Sigal Liraz Zaltsman, Esther Shohami, Juozas Gordevicius, Jack E. Sherman, Ray Bahado-Singh, and Stewart F. Graham
Publication Date: 9-16-2022
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.

